- Definition of a motion transformer
- Motion transformer types
- Focus: Rack & Pinion
- Focus: Crank & Rod system
- Quiz
- Glossary
Rack & Pinion
Presentation:
The main function of a rack and pinion system is to transform a rotational motion into a translational motion (or vice versa).
This system consists of a toothed wheel called a “pinion” and a toothed rod called a “rack”. When the pinion turns, its teeth mesh with the teeth of the rack and drive the rack in a translational motion.
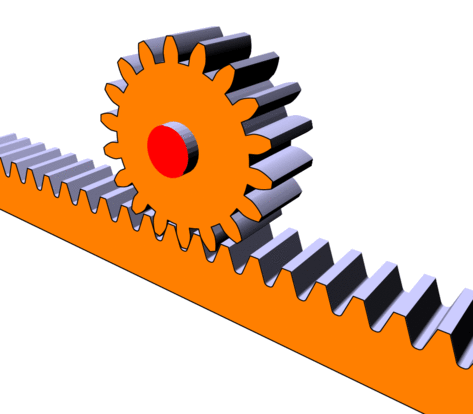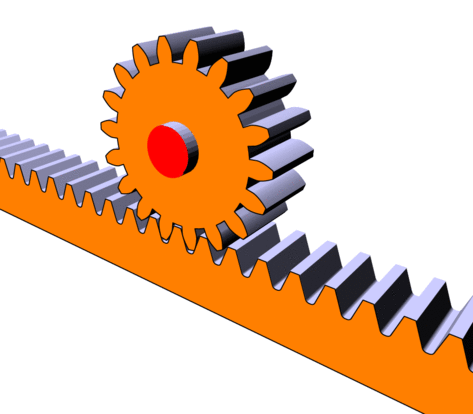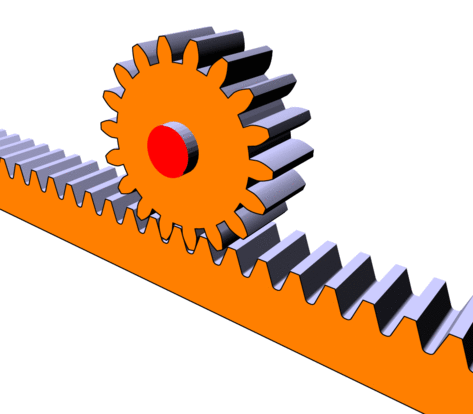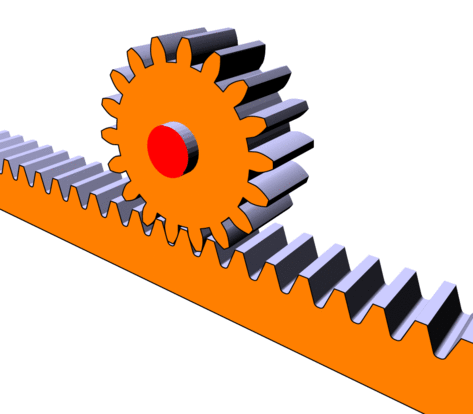
Rack and pinion in motion
Source: http://pstricks.blogspot.com/2020/03/systeme-pignon-cremaillere-en-3d-essai.html
Advantages:
- This type of mechanism allows to transform the movement without sliding between the parts.
- It is a reversible system.
- The strength of this system is relatively great.
Disadvantages:
- The gears that are used may require extensive lubrication.
- This mechanism requires precise adjustment because of the teeth between the wheel and the rack.
- There is a lot of wear.
- It is not a cyclic movement; it is a finite movement (you have to stop when you reach the end of the rack).
Example:
A rack and pinion system is used in the steering mechanism of cars.
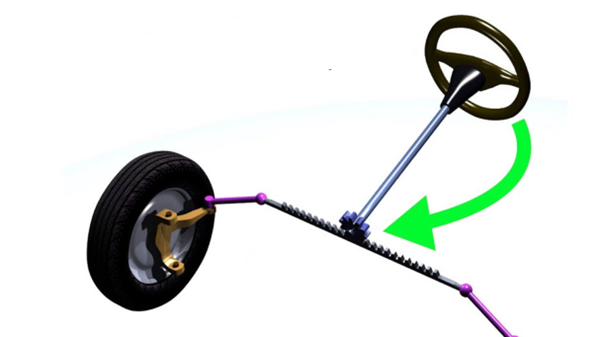
Steering mechanism
Source: https://fr.wikipedia.org/wiki/Direction_(automobile)
How to dimension this system?
Main operation:
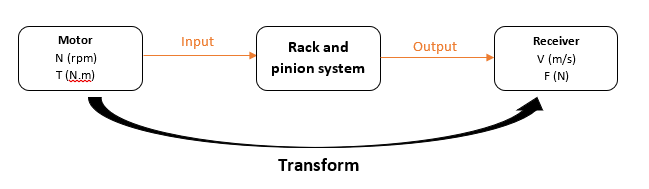
Rack and pinion schema
N = Rotation frequency in rpm (revolutions per minute)
T = Torque in m.N (newton-metre)
V = Speed in m/s (meter per second)
F = Force (Newton)
Geometry:
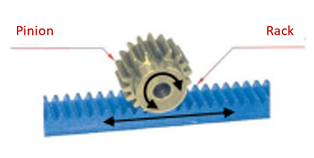
Rack and Pinion system
Source: ssi.stjo.lasalle.free.fr/content/fichiers/FS_1ere/%5BFS15%5D Les engrenages %5BPart_4%5D.pdf
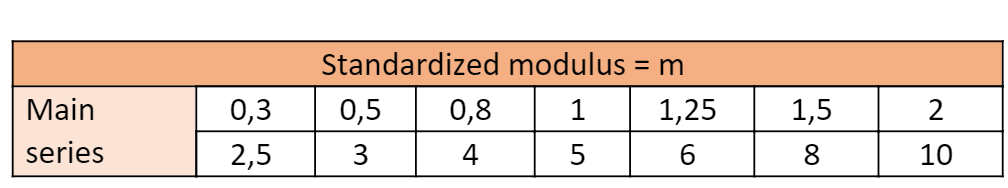
m = modulus
p = step
dpinion = pitch diameter of the pinion
Zpinion = number of pinion teeth
dpinion = m x Zpinion
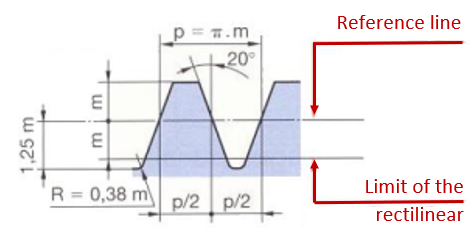
p = step
m = modulus
R = radius
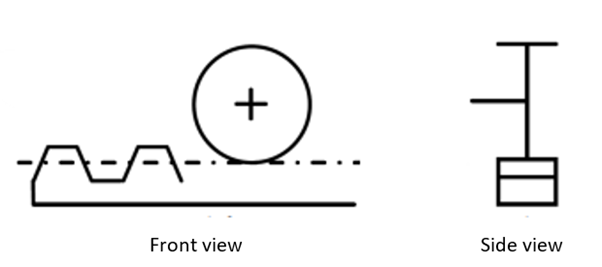
Pinion
Source: ssi.stjo.lasalle.free.fr/content/fichiers/FS_1ere/%5BFS15%5D Les engrenages %5BPart_4%5D.pdf
Mechanical characteristic:
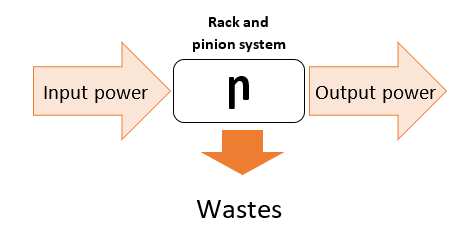
Performance diagram of a pinion rack system
Rotation: P = C . ω
With : P (W), C (m.N), ω (rad/s)
Translation : P = F . V
With : P (W), F (N), V (m/s)
Efficiency : Ps / Pe or Pu / Pa
With : Pu = Useful power
Pa = Absorbed power
The efficiency of this system is very good (>95%). It often takes the value 1 in mechanical models.
Rack speed :
Srack = Rpinion x ωpinion
Rack displacement :
Drack = Rpinion x Ꝋpinion
Srack in m/s
ωpinion : pinion rotation speed in rad/s
Rpinion in m
Ꝋpinion in m
System diagram:
System diagram
Source: ssi.stjo.lasalle.free.fr/content/fichiers/FS_1ere/%5BFS15%5D Les engrenages %5BPart_4%5D.pdf


